Expert advice
In this area of our website we will try to expose the extermination problems to which residences, businesses, businesses and factories are most often exposed, describe the situations and show what can be done to prevent them in the future.
BED BEDS (Cimex lectularius)

DEFINITION:
– Bed bugs are harmful biting insects.
– They bite human beings to feed on their blood but do not live on them.
– The infestation is not a sign of uncleanliness.
– Bedbugs have not been shown to transmit diseases in humans
WHY ARE SPREAD PREVENTED?
– Recently reappeared in most large cities, the bedbug is currently a real nuisance.
– Although the main health risk is inherent in the bites, which can sometimes be counted in very large numbers, this small insect can nevertheless have a very significant impact on the quality of life of the people who are victims of it. In addition to repeated bites, the many annoyances following an infestation can lead to sleep disturbances, anxiety, feelings of insecurity and
dismay.
– If left unchecked, the bedbug reproduces quickly and spreads easily.
– Its resistance to pest control products and methods makes it
difficult to get rid of. As soon as we spot it, we must therefore talk about it, act quickly, and unite our efforts to control it: consultation between the tenant / occupant of the premises, the owner / person in charge of the building and the exterminator is essential.
DESCRIPTION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF BED BEDS
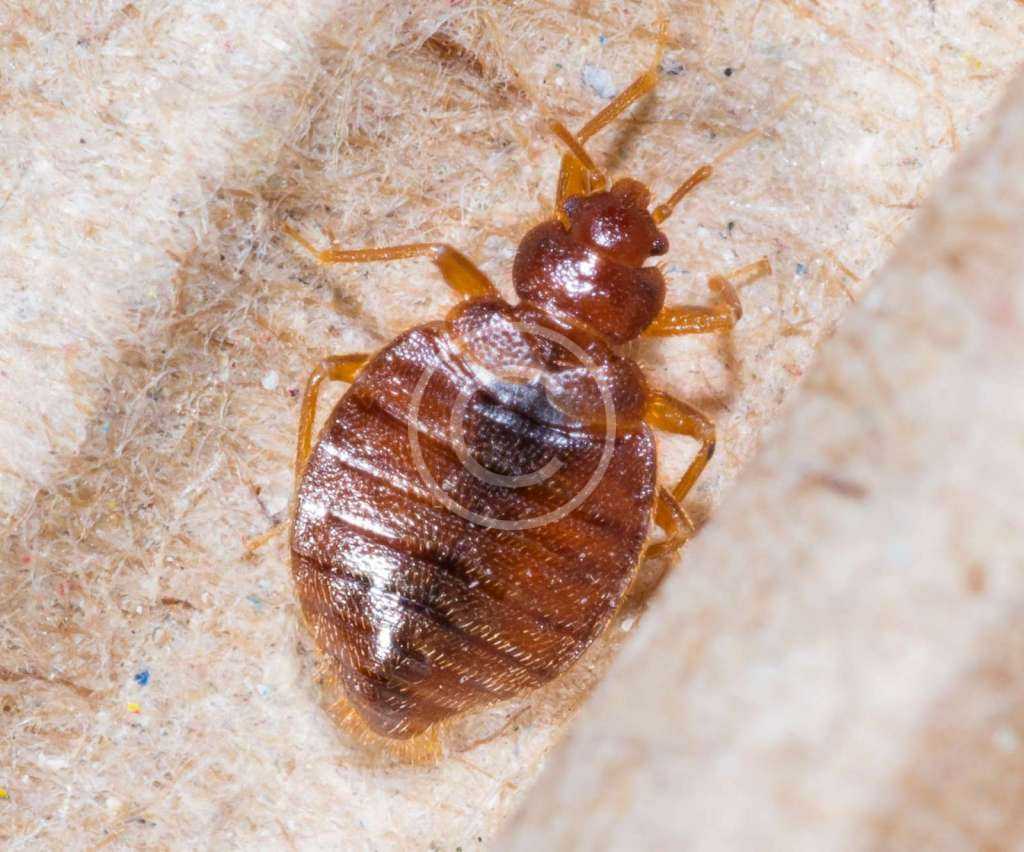
a / - Appearance of Bedbugs:
– Adults: brownish, oval, flattened insects (rounder female), visible to the naked eye, about 4 to 7 millimeters, resembling a flattened apple seed.
– Nymphs: resemble the adult insect, but smaller and yellowish in color.
– Turn reddish when engorged with blood.
– Without wings, they cannot fly or jump. They move by walking.
b / - Behavior of bedbugs:
– Mostly active at night and usually shy away from light.
– Attracted by vibrations, heat, CO2.
– Unlike lice, bedbugs do not stay on the body after a blood meal and do not live on humans (except in rare circumstances). On the other hand, they will stay close to their host if they can feed regularly. As the insect population increases (major infestation), they move away and disperse.
– Unlike fleas, pets do not act as intermediaries
bedbugs to spread to humans.
c / - Life cycle of bedbugs:
Adult females lay two to five eggs per day, or between 300 and 500 eggs
during their lifetime.
Three main stages of development in bedbugs:
– Eggs: whitish, one millimeter long, hatching after 10 to 14 days:
Arranged in a cluster and fixed everywhere (small tight spaces: along the
mattress seams, under the mattress, cracks, crevices, inside walls,
etc.).
– Pupa: looks like the adult insect, but smaller, yellow-white in color.
Feeds on blood like adults, but is more vulnerable to fasting. Past
from nymph to adult after about 4-6 weeks.
– Adult: average lifespan of 5-6 months, depending on environmental conditions and
if it feeds regularly. In some circumstances, can live more than one
year.
d / - Their Food:
– Human blood.
– Duration of the meal: 5 -15 min.
– In general, feed every 3-7 days (or more frequently if T ° C more ↑).
– Maximum activity for biting (eating): between 3:00 a.m. – 6:00 a.m.
– Without food, adults can survive a year or more, going dormant.
e / - Their Habitat:
– Shun the light.
– Take refuge in dark, narrow and inaccessible places. Can
go through a slot the thickness of a credit card.

